What is a MOSFET but a plain old block of silicon with some terminals printed on it. I start here with the most basic of components. Here are the relevant points:
- I want to think about N channel MOSFET so I start with P type material doped at Na=10^16 cm^-3
- Area = A = 1cm x 1cm
- Length = 429cm I chose this because mobility of Boron doping @10^16 = 429cm^2 / V*S
Line of reasoning
- Apply 1 volt
- In 1 second the carriers travel 429cm and thus all the charge in the entire block is swept out and totally replaced.
- Calculate R=V/I
- Compare with value calculated from the page below


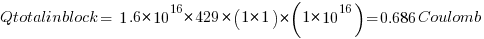
but this is the amount of charge swept out in 1 second from the silicon bar so

Remember 1 volt was applied to get the 429cm/second carrier velocity and thus
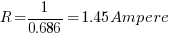 Which agrees with the calculated value from the first web link reference below.
Which agrees with the calculated value from the first web link reference below.
Research Links
- Calculate Input doping, dopant type > compute resistivity
- Resistivity, Sheet Resistance and Mobility Overview – This is a straight forward treatment that I should have read sooner!
- Mobility, Resistivity and sheet resistance
0 Comments